half life formula pharmacology
Formula Half-life Overview Half-life is the time it takes for a drug to reduce in amount by 50. Authors H Boxenbaum 1 M Battle.

Elimination Half Life An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
For drugs with first order kinetics this is a constant.

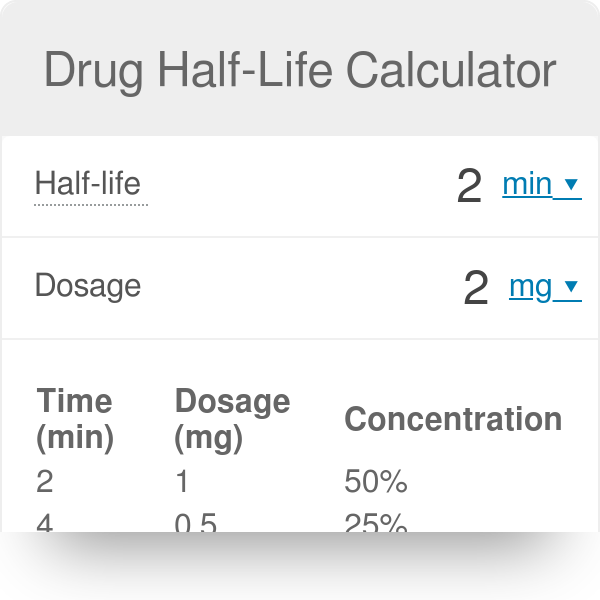
. In order to use our 12 life calculator youll need the following data. Quiz Worksheet - Half. Half-life allows the calculation of the time required for plasma concentrations to reach steady-state after starting or changing a dosing regimen.
A 2 A 0 k t 1 2 displaystyle ce A2 ce A_ 0-kt_ 12 and isolate the time. Half-Life in Pharmacology - Quiz. 5 t T.
Formula Half Life 0693 KE Half Life 0693 0015 462 hours So this means that the drug will take 462 hours to remove roughly half. Drug A has a half-life of 4 hours. This rate is constant in first-order kinetics and is independent of drug concentration in the body.
Accumulation factor 1Fraction lost in one dosing interval 11 - fraction remaining For example the accumulation factor for a drug given once every half-life. Inversely proportional to the fraction of the dose lost in each dosing interval. Drug X has a half-life of 8 hours.
Where N0 refers to the initial quantity of the substance that will decay. If 800mg is administered at 100 am how much of the drug would be eliminated after 24 hours. One can describe exponential decay by any of the three formulas.
If you dont know the half life of the drug take a look at our table below. Apparent half-life t 12. Half-life t 12 is the time required to change the amount of drug in the body by one-half during elimination or during a constant infusionIn the simplest caseand the most useful in designing drug dosage regimensthe body may be considered as a single compartment as illustrated in Figure 32B of a size equal to the volume of distribution V.
The half time of a given drug - this input can be either in minutes hours or days. - The half-life allows us to predict the rate at which a drug will rise and fall in concentration based on the volume of distribution and clearance. Dosage - the amount of the drug administered at the very start.
Pharmacology Drug Half Life Practice Questions. 3 4 Equation 1. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology J Clin Pharmacol.
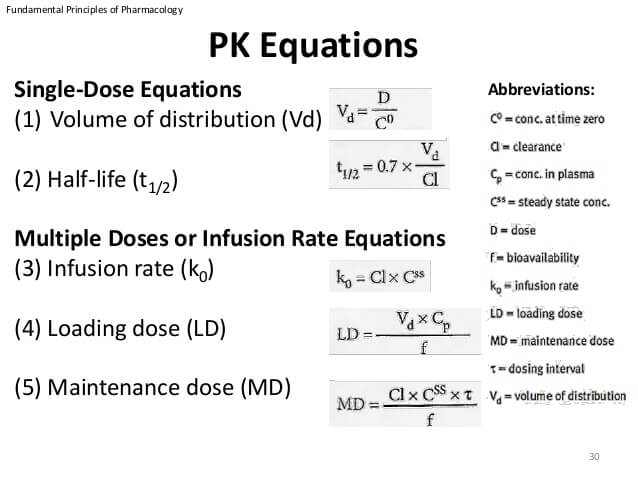
Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half. Ln Ao A k t. T 1 2 ln 2 V D C L displaystyle t_frac 12frac ln 2cdot V_DCL.
N t N0. Margin of Safety in Pharmacology. Half life Extraction ratio.
Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half. Half life formula By using the following decay formula the number of unstable nuclei in a radioactive element left after t can be calculated. Is the disintegration constant.
Where t 1 2. N t N 0 0. An alternative half-life equation exists that relates half-life to other pharmacokinetic parameters known as the volume of distribution and clearance Equation 3.
Elimination rate constant λ. In order to find the half-life we have to replace the concentration value for the initial concentration divided by 2. See the video below for more details.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. ER Dosing rate. 5 t T Nt N_0 times 05tT N t N 0 0.
Half-life t 12 1. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable. Definition Formula Next Lesson.
If 600mg is administered at 800 pm how much of the drug would be eliminated after 24 hours. In some cases such as for controlled-release preparations the rate of decline of the drug plasma. In pharmacology the concepts of half-lives and steady states are relevant to a patient.
By definition t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall by one half. The calculator will set the unit of the result automatically. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology.
In this lesson we will define what a half-life is in pharmacological terms and explain how it is relevant. Fractional rate of drug removal from the body. The measurement of this quantity may take place in grams moles number of atoms etc.
Half life estimation is especially useful when trying to keep constant levels of medicine in the body or when trying to avoid pharmacological interactions between substances. N t N0. N t N0.
The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable. Dosing rate Mghr x dosing interval in hours Loading dose Volume of distribution x target concentration area x permeability coefficient Thickness Protonated concentration. Half-life is determined by clearance CL and volume of distribution V D and the relationship is described by the following equation.
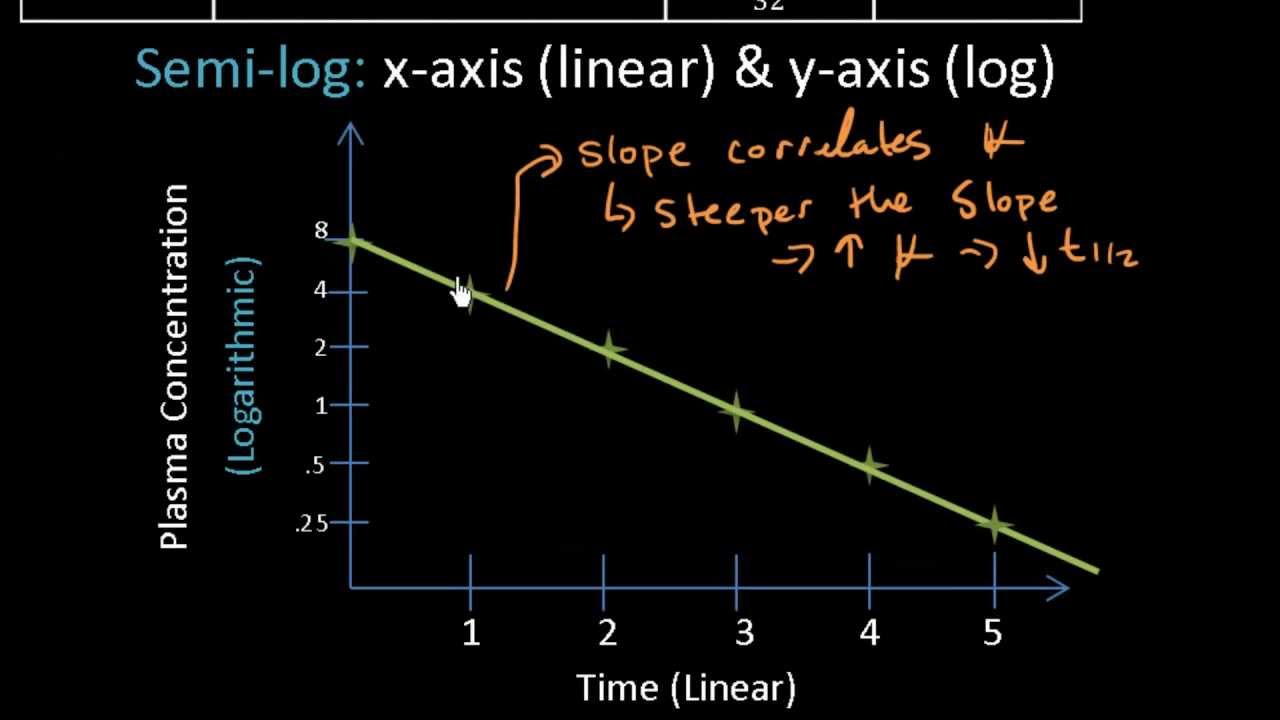
The formula for half life is t 1 2 l n 2 λ 0693 λ. T 1 2 A 0 2 k displaystyle t_ 12 frac. λ is the slope of the plasma concentration-time line on a logarithmic y scale.
Affiliation 1 Wyeth. The medicine half life calculator can be used to follow the plasmatic concentration decrease in percentage for any substance when dosage and half time are input. Dosing rate clearance rate x target concentration.
K first order rate constant. Half life formula half life equation Half life 0693k.
Half Life Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Half Life Drug Calculations Practice Problems Part 6 Youtube
Loading Dose Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It
Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics Epomedicine

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube

Pharmacokinetics Drug Absorption Drug Distribution Drug Metabolis